
Chemistry, 05.05.2021 23:20 bryanmcmillianjr
Calculate the Gibbs free energy change in kJ/mol at 25.0 C for the reaction: C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) ---> 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
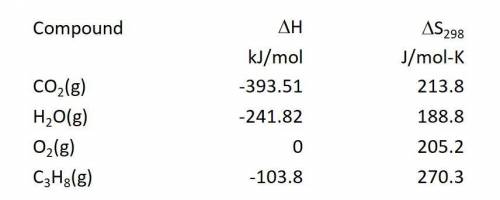

Answers: 3


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 14:30
Clouds form when water vapor to form small droplets. a. humidifies b. condenses c. evaporates d. precipitates
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 20:30
18. use the activity series to predict whether the following synthesis reaction will occur. write the chemical equations for the reaction if it's predicted to occur. (s) + o2(g) -> *note: it is possible.*
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 05:30
A3.37-mg sample of protein was chemically digested to convert its nitrogen into ammonia and then diluted to 100.0 ml. then 10.0 ml of this solution was placed in a 50-ml volumetric flask and treated with 5 ml of phenol solution plus 2 ml of sodium hypochlorite solution. the sample was diluted to 50.0 ml, and the absorbance at 625 nm was measured in a 1.00-cm cuvette and found to be 0.486. for reference, a standard solution was prepared from 10.0 mg of nh4cl (molar mass = 53.49 grams/mole) dissolved in 1.00 l of water. then 10.0 ml of this standard was placed in a 50-ml volumetric flask, treated in the same manner as the unknown, and the absorbance found to be 0.323. finally, a reagent blank was prepared using distilled water in place of unknown, it was treated in the same manner as the unknown, and the absorbance found to be 0.076. calculate the weight percent of nitrogen in the protein.
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 07:30
Which statement is actually true about the relationship between activation energy and reaction rates? low activation energy barriers result in low rates. high activation energy barriers result in low rates. low activation energy barriers result in no reaction. high activation energy barriers result in no reaction.
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
Calculate the Gibbs free energy change in kJ/mol at 25.0 C for the reaction: C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) --->...
Questions


Biology, 17.11.2019 16:31


Chemistry, 17.11.2019 16:31

Mathematics, 17.11.2019 16:31



Mathematics, 17.11.2019 16:31




Mathematics, 17.11.2019 16:31


English, 17.11.2019 16:31


History, 17.11.2019 16:31


Social Studies, 17.11.2019 16:31




