Directed Reading for Key Terms
Content Mastery Motion
d. speed
d. speed
12. incl...

Physics, 13.09.2021 14:00 jngonzo1226
Directed Reading for Key Terms
Content Mastery Motion
d. speed
d. speed
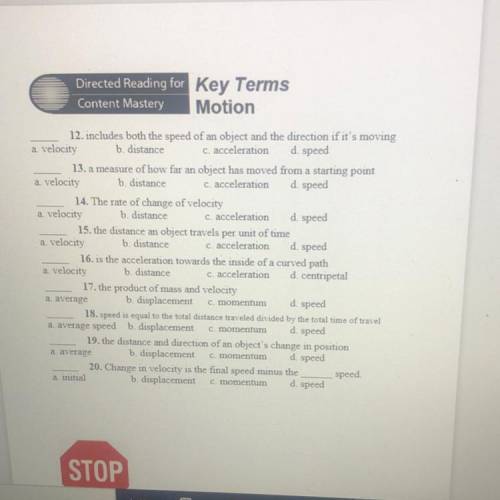
12. includes both the speed of an object and the direction if it's moving
a velocity b. distance c. acceleration d. speed
13. a measure of how far an object has moved from a starting point
a velocity b. distance c. acceleration
d. speed
14. The rate of change of velocity
a velocity
b. distance c. acceleration
15. the distance an object travels per unit of time
a. velocity b. distance c. acceleration
16. is the acceleration towards the inside of a curved path
a velocity b. distance c. acceleration d. centripetal
17. the product of mass and velocity
a. average
b. displacement c. momentum
d. speed
18. speed is equal to the total distance traveled divided by the total time of travel
a average speed b. displacement c. momentum
d. speed
19. the distance and direction of an object's change in position
a average b. displacement c. momentum d. speed
20. Change in velocity is the final speed minus the speed
a. initial
b. displacement c. momentum d. speed

Answers: 1


Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 02:00
Chapter 23, problem 075 the figure shows a geiger counter, a device used to detect ionizing radiation (radiation that causes ionization of atoms). the counter consists of a thin, positively charged central wire surrounded by a concentric, circular, conducting cylindrical shell with an equal negative charge. thus, a strong radial electric field is set up inside the shell. the shell contains a low-pressure inert gas. a particle of radiation entering the device through the shell wall ionizes a few of the gas atoms. the resulting free electrons (e) are drawn to the positive wire. however, the electric field is so intense that, between collisions with gas atoms, the free electrons gain energy sufficient to ionize these atoms also. more free electrons are thereby created, and the process is repeated until the electrons reach the wire. the resulting "avalanche" of electrons is collected by the wire, generating a signal that is used to record the passage of the original particle of radiation. suppose the radius of the central wire is 24 âµm, the inner radius of the shell 2.3 cm, and the length of the shell 14 cm. if the electric field at the shell's inner wall is 2.8 ă— 104 n/c, what is the total positive charge on the central wire?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 03:00
Do you agree with scientist’s prediction about the warming of alaska and other polar regions?
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 16:30
A14 kg rock starting from rest free falls through a distance of 5.0 m with no air resistance. find the momentum change of the rock caused by its fall and the resulting change in the magnitude of earths velocity. earth mass is 6.0 * 10^24 kg. show your work assuming the rock earth system is closed.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 19:40
It may seem strange that the selected velocity does not depend on either the mass or the charge of the particle. (for example, would the velocity of a neutral particle be selected by passage through this device? ) the explanation of this is that the mass and the charge control the resolution of the device--particles with the wrong velocity will be accelerated away from the straight line and will not pass through the exit slit. if the acceleration depends strongly on the velocity, then particles with just slightly wrong velocities will feel a substantial transverse acceleration and will not exit the selector. because the acc
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Questions

English, 07.11.2019 19:31





Chemistry, 07.11.2019 19:31

English, 07.11.2019 19:31







Spanish, 07.11.2019 19:31


Mathematics, 07.11.2019 19:31

English, 07.11.2019 19:31





