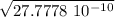Physics, 18.03.2021 01:20 dawood7068
When conducting objects (such as metals) are connected for a brief time, charge can be made to flow quite easily from one to the other, even if the objects are in contact for an extremely brief amount of time. To that end, consider two identical metallic ball bearings (i. e., two very tiny metallic solid spheres) having unknown charges 41 and 42. It is found that when they are placed 1 m apart, they experience a 25-N attractive force.
(a) What can you conclude about the charges on these metal marbles from the information given?
(b) The ball bearings are made to touch very briefly and then are separated by 1 m again. What can you conclude about the charges now? Explain.
(c) Suppose that when the charges are 1 m apart, after briefly touching, they again feel a force of 25 N Determine the charges 41 and 42.

Answers: 1


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 20:30
Aball is thrown straight up into the air with a speed of 21 m/s. if the ball has a mass of 0.1 kg, how high does the ball go? acceleration due to gravity is g = 9.8 m/s^2. a. 22.5 m b. 20.0 m c. 25.0 m d. 17.5 m
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 10:00
One object has a mass of 1 kg and another object has a mass of 3 kg. if the speeds are the same, which of the following is true about their kinetic energy?
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 21:20
Would it be correct to say the doppler effect is the apparent change in the speed of a wave due to the motion of the source? be sure to fully explain your position using at least 3 complete content related sentences.
Answers: 3

Physics, 23.06.2019 01:00
Learning goal: to understand newton's 1st law. newton's principia states this first law of motion: an object subject to no net force maintains its state of motion, either at rest or at constant speed in a right line. this law may be restated as follows: if the sum of all forces acting on an object is zero, then the acceleration of that object is zero. mathematically this is just a special case of the 2nd law of motion, f⃗ =ma⃗ , when f⃗ =0. when studying newtonian mechanics, it is best to remember the 1st law in two ways: if the net force (i.e., sum of all forces) acting on an object is zero, the object will keep moving with constant velocity (which may be zero). if an object is moving with constant velocity, that is, with zero acceleration, then the net force acting on that object must be zero. complete the following sentences to see if you can apply these ideas. part a if a car is moving to the left with constant velocity, one can conclude that
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
When conducting objects (such as metals) are connected for a brief time, charge can be made to flow...
Questions


Mathematics, 27.03.2021 18:40

Biology, 27.03.2021 18:40


History, 27.03.2021 18:40

Mathematics, 27.03.2021 18:40


Health, 27.03.2021 18:40

Social Studies, 27.03.2021 18:40

Mathematics, 27.03.2021 18:40

Arts, 27.03.2021 18:40


History, 27.03.2021 18:40



Mathematics, 27.03.2021 18:40

Mathematics, 27.03.2021 18:40



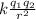
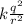
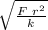
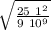 =
=