
Physics, 29.08.2019 20:20 naimareiad
A5.0-g particle moving 60 m/s collides with a 2.0-g particle initially at rest. after the collision, each of the particles has a velocity that is directed 30° from the original direction of motion of the 5.0-g particle. what is the speed of the 2.0-g particle after the collision?

Answers: 3


Another question on Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 15:30
Match the atomic particles with their characteristics. 1. made of two protons and two neutrons neutron 2. similar to an electron; positive charge neutrino 3. orbits nucleus; negative charge positron 4. bundle of energy; zero charge proton 5. found in nucleus; positive charge meson 6. very unstable; +, -, or zero charge gamma 7. found in nucleus; zero charge electron 8. negative particle; negative charge beta 9. atomic energy converted to mass alpha
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 07:30
Automobile fuel efficiency is often measured in miles that the car can be driven per gallon of fuel (mpg). heavier cars tend to have lower fuel efficiencies (lower mpg ratings). which variable (weight or fuel efficiency) is most naturally considered the explanatory (predictor) variable in this context?
Answers: 3


Physics, 22.06.2019 19:50
An electron moves with a constant horizontal velocity of 3.0 × 106 m/s and no initial vertical velocity as it enters a deflector inside a tv tube. the electron strikes the screen after traveling 26 cm horizontally and 19 cm vertically upward with no horizontal acceleration. what is the constant vertical acceleration provided by the deflector? (the effects of gravity can be ignored.)
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
A5.0-g particle moving 60 m/s collides with a 2.0-g particle initially at rest. after the collision,...
Questions

History, 12.10.2020 22:01

Biology, 12.10.2020 22:01


Mathematics, 12.10.2020 22:01

Mathematics, 12.10.2020 22:01


English, 12.10.2020 22:01

Arts, 12.10.2020 22:01




Mathematics, 12.10.2020 22:01




English, 12.10.2020 22:01

History, 12.10.2020 22:01

Mathematics, 12.10.2020 22:01


Mathematics, 12.10.2020 22:01

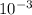 kg
kg

