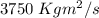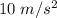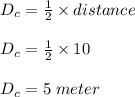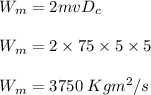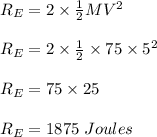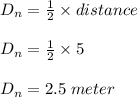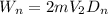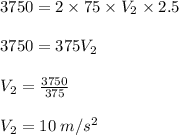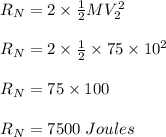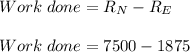Physics, 12.08.2019 22:10 gabrieljerron
Two astronauts, each having a mass of 75.0 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. they are isolated in space, orbiting their center of mass at speeds of 5.00 m/s. treating the astronauts as particles, calculate (a) the magnitude of the angular momentum of the system and (b) the rotational energy of the system. by pulling on the rope, one of the astronauts shortens the distance between them to 5.00 m. (c) what is the new angular momentum of the system? (d) what are the astronauts’ new speeds? (e) what is the new rotational energy of the system? (f) how much work does the astronaut do in shortening the rope?

Answers: 2


Another question on Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 07:50
The ratio of lift to drag l/d for a wing or airfoil is an important aerodynamic parameter, indeed, it is a direct measure of the aerodynamic efficiency of the wing. if a wing is pitched through a range of angle of attack, l/d first increases, then goes through a maximum, and then decreases. consider an infinite wing with an naca 2412 airfoil. estimate the maximum value of l/d. assume that the reynolds number is 9x10^6.
Answers: 2


Physics, 22.06.2019 14:30
Which one of the following terms is used to indicate the natural tendency of an object to remain at rest or in motion at a constant speed along a straight line? velocity acceleration equilibrium force inertia
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 17:10
As the distance from a magnet increases, what happens to the magnet force?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Two astronauts, each having a mass of 75.0 kg, are connected by a 10.0-m rope of negligible mass. th...
Questions


History, 21.02.2021 02:40

Mathematics, 21.02.2021 02:40


Health, 21.02.2021 02:40


Computers and Technology, 21.02.2021 02:40


Geography, 21.02.2021 02:40

English, 21.02.2021 02:40

History, 21.02.2021 02:40

Mathematics, 21.02.2021 02:40


Mathematics, 21.02.2021 02:40


Mathematics, 21.02.2021 02:40

English, 21.02.2021 02:40


Biology, 21.02.2021 02:40