When expressed as a single logarithm, ln x + 5 ln y - 1/2 ln z is equivalent to:
...

Mathematics, 12.10.2019 14:30 natalymorales96
When expressed as a single logarithm, ln x + 5 ln y - 1/2 ln z is equivalent to:
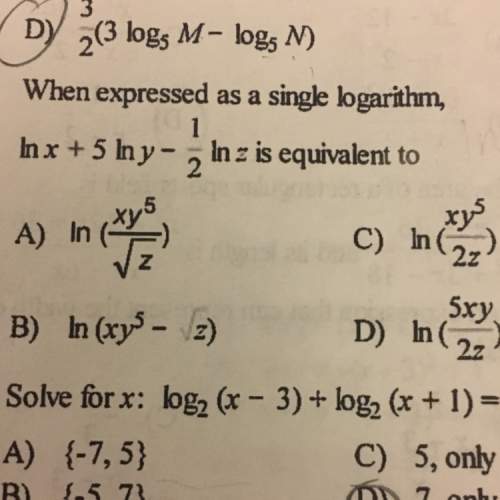

Answers: 1


Another question on Mathematics


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:30
Does the function satisfy the hypotheses of the mean value theorem on the given interval? f(x) = 4x^2 + 3x + 4, [−1, 1] no, f is continuous on [−1, 1] but not differentiable on (−1, 1). no, f is not continuous on [−1, 1]. yes, f is continuous on [−1, 1] and differentiable on (−1, 1) since polynomials are continuous and differentiable on . there is not enough information to verify if this function satisfies the mean value theorem. yes, it does not matter if f is continuous or differentiable; every function satisfies the mean value theorem.
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:00
Which of the functions graphed below has a removable discontinuity?
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:00
Y= 4x + 3 y = - 1 4 x - 5 what is the best description for the lines represented by the equations?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Questions

Mathematics, 14.11.2019 19:31

Mathematics, 14.11.2019 19:31

Social Studies, 14.11.2019 19:31


Mathematics, 14.11.2019 19:31





Mathematics, 14.11.2019 19:31

History, 14.11.2019 19:31

History, 14.11.2019 19:31

History, 14.11.2019 19:31

Physics, 14.11.2019 19:31

History, 14.11.2019 19:31

Mathematics, 14.11.2019 19:31


Mathematics, 14.11.2019 19:31


Spanish, 14.11.2019 19:31



