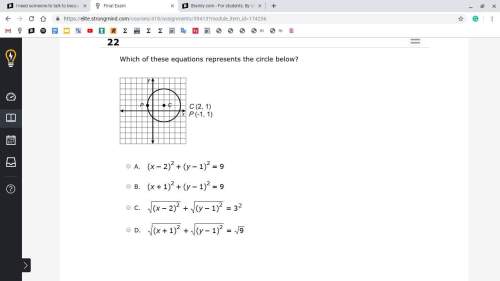
Mathematics, 10.11.2020 09:20 WolfMeadows
What is the solution to the linear equation?
StartFraction 2 Over 5 EndFraction plus p equals StartFraction 4 Over 5 EndFraction plus StartFraction 3 Over 5 EndFraction p. + p = + p
(THE ANSWER IS P = 1 FOR ANYONE HAVING TROUBLE EDGE 2020)
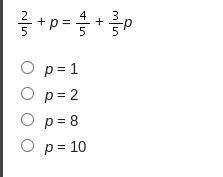

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 13:50
James wants to promote his band on the internet. site a offers website hosting for $4.95 per month with a $49.95 startup fee. site b offers website hosting for $9.95 per month with no startup fee. for how many months would james need to keep the website for site a to be a better choice than site b? 1. define a variable for the situation. 2. write an inequality that represents the situation. 3.solve the inequality to find out how many months he needs to keep the website for site a to be less expensive than site b. 4. using words, describe how many months he needs to keep the website for site a to be less expensive than site b.
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 14:30
Which functions are even? check all of the boxes that apply. f(x) = x4 – x? f(x) = x2 – 3x + 2 f(x) = (x - 2) f(x) = x done
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:30
Does the function satisfy the hypotheses of the mean value theorem on the given interval? f(x) = 4x^2 + 3x + 4, [−1, 1] no, f is continuous on [−1, 1] but not differentiable on (−1, 1). no, f is not continuous on [−1, 1]. yes, f is continuous on [−1, 1] and differentiable on (−1, 1) since polynomials are continuous and differentiable on . there is not enough information to verify if this function satisfies the mean value theorem. yes, it does not matter if f is continuous or differentiable; every function satisfies the mean value theorem.
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:00
Match the vocabulary to the proper definition. in probability, two events in which 1. conditional probability the outcome of one event is independent of the outcome of a second event. 2. dependent events in probability, two events in which the outcome of one event is dependent on the outcome of a second event. the probability of an event in which the outcome of the event is conditional on the outcome of one or more different events. 3. independent events
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
What is the solution to the linear equation?
StartFraction 2 Over 5 EndFraction plus p equals Start...
Questions

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50

Social Studies, 04.12.2020 05:50


Advanced Placement (AP), 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50



Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50


Arts, 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50

Mathematics, 04.12.2020 05:50



Spanish, 04.12.2020 05:50

History, 04.12.2020 05:50