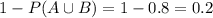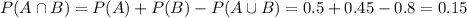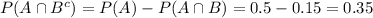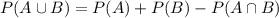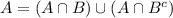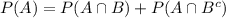Mathematics, 15.04.2020 18:01 Sumitco9578
A shopper is randomly selected from a market. Let A be the event the selected shopper has a Visa credit card, and B be the event the shopper has a Mastercard credit card. Suppose P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.45, and P(A ∪ B) = 0.8.a. What is the probability that the shopper has neither type of card? b. What is the probability that the shopper has both types of card? c. What is the probability the individual has a Visa card but not a Mastercard? (Hint: You will use the answer from part b.) d. Are the events of having a Visa card and a Mastercard mutually exclusive?

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 13:30
Suppose that f(0) = −3 and f '(x) ≤ 8 for all values of x. how large can f(4) possibly be? solution we are given that f is differentiable (and therefore continuous) everywhere. in particular, we can apply the mean value theorem on the interval [0, 4] . there exists a number c such that
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:20
This graph shows which inequality? a ≤ –3 a > –3 a ≥ –3 a < –3
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 00:30
Abcd is reflected across the x- axis, then rotated 90 clockwise about the orgin, and finally reflected across the line y= x to form a’ b’ c’ .
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 22.06.2019 03:10
The coverage of a base station of a telecommunication company forms a disk with a radius of (kilometers). let be the distance of a cellphone from a base station. assume that the location of cellphones in use are randomly uniformly distributed within the disk. calculate the mean and variance for the random variable.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
A shopper is randomly selected from a market. Let A be the event the selected shopper has a Visa cre...
Questions

Mathematics, 16.01.2022 07:20

Mathematics, 16.01.2022 07:20


Mathematics, 16.01.2022 07:20

Mathematics, 16.01.2022 07:20

English, 16.01.2022 07:20



Biology, 16.01.2022 07:20

Mathematics, 16.01.2022 07:20





History, 16.01.2022 07:30


Business, 16.01.2022 07:30

Mathematics, 16.01.2022 07:30