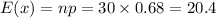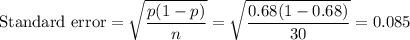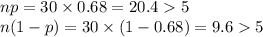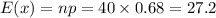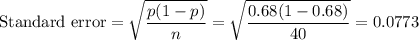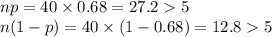Mathematics, 16.03.2020 20:09 salinasroel22
Consider a population proportion p = 0.68. a-1. Calculate the expected value and the standard error of P− with n = 30. (Round "expected value" to 2 decimal places and "standard deviation" to 4 decimal places.) a-2. Is it appropriate to use the normal distribution approximation for P− ? Yes No b-1. Calculate the expected value and the standard error of P− with n = 40. (Round "expected value" to 2 decimal places and "standard deviation" to 4 decimal places.) b-2. Is it appropriate to use the normal distribution approximation for P− ?

Answers: 3


Another question on Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 15:00
What are the coordinates of the point is 1/4 of the way from a (-6, -3) to b (6, 1)? a. (-3, -2) b. (0, -2) c. (-1, 0) d. (3, 2)
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:40
One of the inventors of integrated circuits observed that the number of transistors that fit on an integrated circuit will double every 24 months. what type of relationship most appropriately models this situation?
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:00
In trapezoid abcd, ac is a diagonal and ∠abc≅∠acd. find ac if the lengths of the bases bc and ad are 12m and 27m respectively.
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:20
The suare root of 9x plus 7 plus the square rot of 2x equall to 7
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
Consider a population proportion p = 0.68. a-1. Calculate the expected value and the standard error...
Questions

Social Studies, 20.06.2020 21:57



Mathematics, 20.06.2020 21:57



Mathematics, 20.06.2020 21:57


English, 20.06.2020 21:57


Mathematics, 20.06.2020 21:57








History, 20.06.2020 21:57