Engineering, 26.01.2021 15:50 nguyendavis17
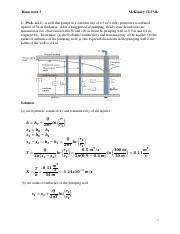
5. After a long period of pumping from an unconfined aquifer at a constant rate of 850 m3/day, the cone of depression reaches equilibrium. The aquifer has an initial saturated thickness of 20m and a hydraulic conductivity of 8.65 m/day. During the equilibrium, the water levels in an observation well 50m away and in the pumping well are measured as 18.4 and 9.9 m. Determine (a) the radius of influence of the pumping, (b) the radial distance where the steady state drawdown is 5 cm, (c) the expected drawdown in the pumping well (rw =0.4), and (d) the total well head losses.

Answers: 1


Another question on Engineering

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10
Give heat transfer applications for the following, (i) gas turbines (propulsion) ) gas turbines (power generation). (iii) steam turbines. (iv) combined heat and power (chp). (v) automotive engines
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20
Along 8-cm diameter steam pipe whose external surface temperature is 900c connects two buildings. the pipe is exposed to ambient air at 70c with a wind speed of 50 km/hr blowing across the pipe. determine the heat loss from the pipe per unit length. (b) air at 500c enters a section of a rectangular duct (15 cm x 20 cm) at an average velocity of 7 m/s. if the walls of the duct are maintained at 100c. a) the length of the tube for an exit temperature of the air to be 40 0c. b)the rate of heat transfer from the air. c) the fan power needed to overcome the pressure drop in this section of the duct.
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 19:10
Plan an experiment to measure the surface tension of a liquid similar to water. if necessary, review the ncfmf video surface tension for ideas. which method would be most suitable for use in an undergraduate laboratory? what experimental precision could be expected?
Answers: 2

Engineering, 04.07.2019 19:20
At steady state, air at 200 kpa, 325 k, and mass flow rate of 0.5 kg/s enters an insulated duct having differing inlet and exit cross-sectional areas. the inlet cross-sectional area is 6 cm2. at the duct exit, the pressure of the air is 100 kpa and the velocity is 250 m/s. neglecting potential energy effects and modeling air as an 1.008 kj/kg k, determine ideal gas with constant cp = (a) the velocity of the air at the inlet, in m/s. (b) the temperature of the air at the exit, in k. (c) the exit cross-sectional area, in cm2
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
5. After a long period of pumping from an unconfined aquifer at a constant rate of 850 m3/day, the c...
Questions

Mathematics, 16.11.2019 11:31

Physics, 16.11.2019 11:31


History, 16.11.2019 11:31

Mathematics, 16.11.2019 11:31



History, 16.11.2019 11:31





Mathematics, 16.11.2019 11:31

Mathematics, 16.11.2019 11:31



Chemistry, 16.11.2019 11:31



Mathematics, 16.11.2019 11:31