Chemistry, 02.06.2021 04:50 myaaa13754
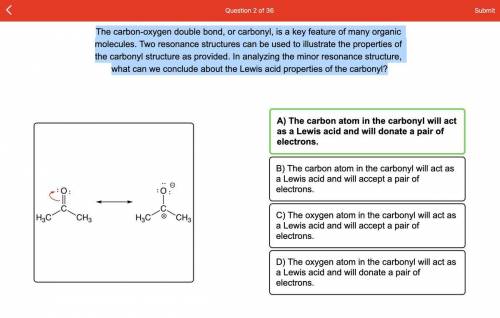
The carbon-oxygen double bond, or carbonyl, is a key feature of many organic molecules. Two resonance structures can be used to illustrate the properties of the carbonyl structure as provided. In analyzing the minor resonance structure, what can we conclude about the Lewis acid properties of the carbonyl

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 16:30
Asample of silver (with work function ? = 4.52 ev) is exposed to an ultraviolet light source (? = 200 nm), which results in the ejection of photoelectrons. what changes will be observed if: silver is replaced with copper (? = 5.10 ev) more photoelectrons ejected no photoelectrons are emitted fewer photoelectrons ejected more energetic photoelectrons (on average) less energetic photoelectrons (on average)
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 19:30
If the element whose electric configuration ends in the d sublevel, the element is calssified as? a.inner transition b.noble gases c.representative d. transition
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 04:00
Tin has ten stable isotopes. the heaviest, 124sn, makes up 5.80% of naturally occuring tin atoms. how many atoms of 124sn are present in 82.0 g of naturally occurring tin? what is the total mass of the 124sn atoms in this sample?
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 14:30
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor reduce an enzyme’s activity?
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
The carbon-oxygen double bond, or carbonyl, is a key feature of many organic molecules. Two resonanc...
Questions

Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31

Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31


Physics, 07.01.2020 04:31


History, 07.01.2020 04:31


Health, 07.01.2020 04:31


Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31

Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31



Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31

Social Studies, 07.01.2020 04:31


Physics, 07.01.2020 04:31

Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31

History, 07.01.2020 04:31

Mathematics, 07.01.2020 04:31