Classifying reactions lab !
classifying reactions
safety reminder: wear safety glasses and use ammonia in a well-ventilated area. be sure to read science safety (link on page 1 of this lesson or page 872 in textbook)
objectives:
balance chemical equations (u4l1)
identify different types of reactions (u4l2)
describe evidence that a chemical reaction took place (u2l3)
day 1
part 1 reaction between iron and oxygen (record observations for 5 days)
materials:
small glass jar
dish with sides (a pie plate works well)
steel wool
water
procedure:
1. dip a piece of steel wool in vinegar for about 5 minutes to remove any coatings and then rinse it with water.
2. tape the piece of steel wool to the bottom of the jar.
3. fill the dish about halfway with water.
4. put the jar upside down in the dish.
5. observe the water levels in the dish and the jar and observe the steel wool in the jar for 5 days.
record your observations each day in the table below.
observations:
day|water level in dish (cm)|water level in jar (cm)|appearance of steel wool
1 | | |
2 | | |
3 | | |
4 | | |
5 | | |
analysis/conclusions:
1. balance the equation for the reaction between iron and oxygen.
+ →
2. classify the reaction that occurred between the iron and oxygen.
3. what evidence was there that a reaction took place?
part ii: reaction of hydrogen peroxide
materials:
hydrogen peroxide (1/3 cup)
small pieces of raw potato (yeast or beef liver may be substituted)
small bowl
procedure:
pour one third of a cup of hydrogen peroxide into a small bowl.
cut up several small pieces of raw potato and place them in the hydrogen peroxide.
3. record your observations.
observations:
appearance of potato and hydrogen peroxide combination
analysis/conclusion:
1. the potato (as well as yeast and beef liver) contains an enzyme called catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide. balance the equation, if necessary, for the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide.
→ +
2. classify the reaction that occurred.
3. what evidence was there that a reaction was taking place?
day 2
part iii: reaction between zinc and acetic acid
materials:
a penny dated after 1983
metal file or coarse sandpaper
vinegar
procedure:
use a file or sandpaper to completely remove the copper from the edge of a penny. once the copper is removed you can see the silvery zinc that composes the core of the penny.
place the penny into a small jar of vinegar so that the penny sits upright. this will allow the hydrogen gas to readily escape and increase the rate of reaction.
allow the container to stand undisturbed for 30 minutes.
while the mixture is standing, complete steps 1 and 2 of part iv of the lab. be sure to record on the next page your observations for part iii after 30 minutes.
observations:
appearance of penny in vinegar after 30 minutes
analysis/conclusions:
1. balance the equation for the reaction between zinc and acetic acid.
+ → (ch3coo)2 +
2. classify the reaction between zinc and acetic acid.
3. what evidence was there that a reaction was taking place?
part iv: reaction between magnesium sulfate and ammonia
materials:
epsom salts (mgso4),
ammonia (nh4oh)
small jar or cup
measuring cup
procedure:
dissolve 1 teaspoon of epsom salts in a half cup of water.
add 2 teaspoons of ammonia to the epsom salts solution and stir thoroughly. record your observations.
allow the mixture to stand for 30 minutes and record your observations.
observations:
appearance after initial mixing
appearance after 30 minutes 
analysis/conclusions:
1. balance the equation for the reaction between magnesium sulfate and ammonia.
(2 points)
+ → )2so4 + (oh)2
2. classify the reaction between magnesium sulfate and ammonia.
3. what evidence was there to indicate that the epsom salts and ammonia reacted?

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 03:30
The atomic radius of sodium is 186 pm and of chlorine is 100 pm. the ionic radius for na+ is 102 pm and for cl– is 181 pm. in going from na to cl in period 3, why does the atomic radius decrease while the ionic radius increases? a. the inner electrons in the sodium cation shield its valence electrons more effectively than the inner electrons in the chloride anion do. b. the inner electrons shield the valence electrons more effectively in the chlorine atom than in the chloride anion. c. the outermost electrons in chloride experience a smaller effective nuclear charge than those in the sodium cation do. d. the outermost electrons in chloride experience a larger effective nuclear charge than those in the sodium cation do. e. monatomic ions are bigger than the atoms from which they are formed.
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 10:00
Ahydrogen atom has 1 electron. how many bonds can hydrogen form? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5
Answers: 3

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 12:30
Place the elements below in order of decreasing ionization energy. aluminum(al) chlorine(cl) magnesium (mg) sulfur(s)
Answers: 1

You know the right answer?
Classifying reactions lab !
classifying reactions
safety reminder: wear safety g...
classifying reactions
safety reminder: wear safety g...
Questions

Mathematics, 07.05.2021 04:10




History, 07.05.2021 04:10

History, 07.05.2021 04:10

Mathematics, 07.05.2021 04:10

Computers and Technology, 07.05.2021 04:10

History, 07.05.2021 04:10

Mathematics, 07.05.2021 04:10

Social Studies, 07.05.2021 04:10

Social Studies, 07.05.2021 04:10



Biology, 07.05.2021 04:10



Mathematics, 07.05.2021 04:10

SAT, 07.05.2021 04:10

English, 07.05.2021 04:10


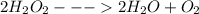
 .
.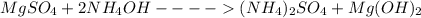 .
.