Chemistry, 22.09.2020 21:01 briannasineiro7937
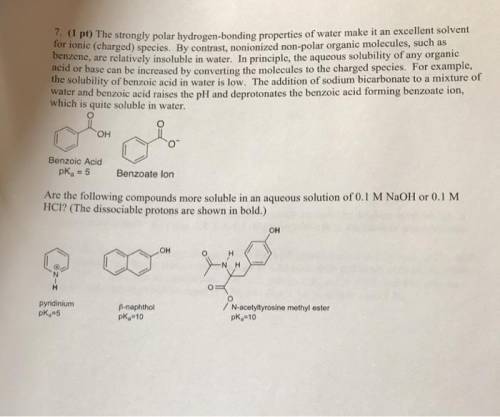
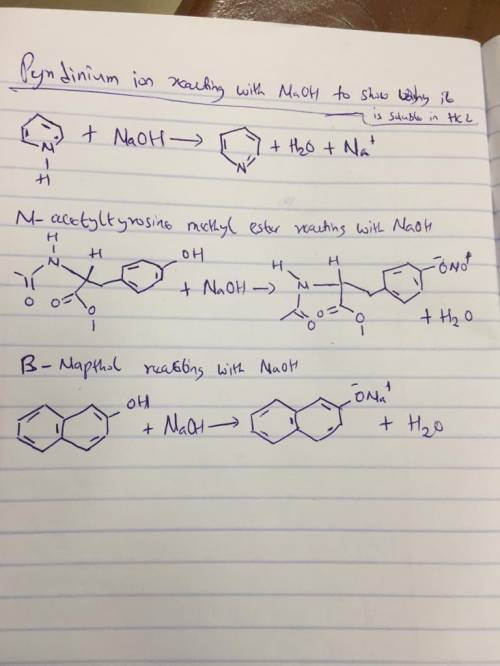
The strongly polar, hydrogen-bonding properties of water make it an excellent solvent for ionic (charged) species. By contrast, nonionized, nonpolar organic molecules, such as benzene, are relatively insoluble in water. In principle, the aqueous solubility of any organic acid or base can be increased by converting the molecules to charged species. For example, the solubility of benzoic acid in water is low. The addition of sodium bicarbonate to a mixture of water and benzoic acid raises the pH and deprotonates the benzoic acid to form benzoate ion, which is quite soluble in water?

Answers: 2


Another question on Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 17:00
What is the nature of the ca-cl bond in a molecule of calcium chloride (cacl2) if the electronegativity value of calcium is 1.0 and that of chlorine is 3.16?
Answers: 1


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 22:10
Which aqueous solution of ki freezes at the lowest temperature? 1) 1 mol of ki in 500. g of water 2) 2 mol of ki in 500. g of water 3) 1 mol of ki in 1000. g of water 4) 2 mol of ki in 1000. g of water
Answers: 3

You know the right answer?
The strongly polar, hydrogen-bonding properties of water make it an excellent solvent for ionic (cha...
Questions







History, 30.11.2020 18:00


History, 30.11.2020 18:00



Mathematics, 30.11.2020 18:00


Computers and Technology, 30.11.2020 18:00

Mathematics, 30.11.2020 18:00

Mathematics, 30.11.2020 18:00




Mathematics, 30.11.2020 18:00