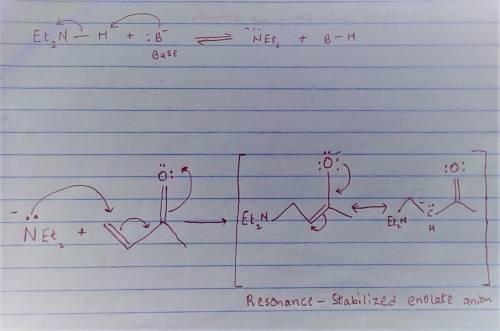
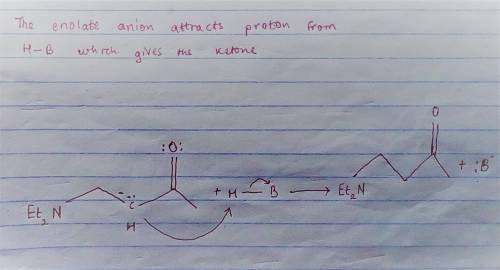
Chemistry, 19.06.2020 00:57 josephvcarter
Carbon-carbon double bonds are electron-rich regions and are attacked by electrophiles (for example, ); they are not attacked by nucleophiles (for example, diethylamine, ). + reaction arrow with electrophilic addition written above + no reaction However, when the carbon-carbon double bond has a carbonyl group adjacent to it, the double bond reacts readily with nucleophiles by nucleophilic addition. + reaction arrow with nucleophilic addition written above For the following reaction, draw the structure of the resonance contributor that is attacked by diethylamine. + Include all valence lone pairs in your answer.

Answers: 1


Another question on Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 17:30
Observation and experimentation have led many scientists to accept a theory about the origin of the universe. this theory is called the big bang theory. scientific evidence collected and observed by scientists around the world suggests that the universe is ever expanding from a hot and dense initial state. what makes this a scientific theory? (2 points)
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 22:00
Does the number of ions in solution increase, decrease, or remain constant? it continuously decreases. it continuously increases. it decreases at first, then increases. it increases at first, then decreases.
Answers: 3

You know the right answer?
Carbon-carbon double bonds are electron-rich regions and are attacked by electrophiles (for example,...
Questions


Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20


Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20

Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20


English, 28.06.2021 22:20


Biology, 28.06.2021 22:20

Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20


Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20

Computers and Technology, 28.06.2021 22:20


Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20


History, 28.06.2021 22:20

Mathematics, 28.06.2021 22:20


 - carbon of the conjugate thereby resulting into a resonance stabilized enolate anion.
- carbon of the conjugate thereby resulting into a resonance stabilized enolate anion.