
Business, 07.04.2021 03:40 shaylasimonds6103
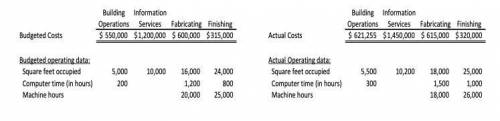
Fabricating and Finishing are two production departments of Michael Manufacturing. Building Operations and Information Services are support departments. “Building Operations” provides services to both support and production departments. YOU ARE THE MANAGER OF THE FABRICATING DEPARTMENT!
“Information Services” does NOT provide any services for non-production areas of the company.
The company employs departmental overhead rates and both producing departments use machine hours to allocate their overhead. Square footage is used to allocate building operations, while computer time is used to allocate information services.
The budgeted and actual cost data of the support departments, departmental overhead and other relevant operating data are as follows:
1. The company is using the Direct Method to allocate support costs. Under this method, how much Building Operations cost will be allocated to Information Services?
2. Michael mentions to Paul that they could really benefit from using the most accurate method, known as the "Reciprocal" or "Algebraic" method. Could Michael benefit from using this method? Yes or No and WHY?
3. Liza suggests that the Step Method be used. Under this method, what will be the POHR that will be used in your Fabricating department for product costing during the year (per machine hour)?
4. Your Building Operations department is a cost center. Thus, at the end of the year you will receive a responsibility-accounting based report comparing your budgeted direct costs and support costs and comparing these to the actual.
5. Based on your computations above, how much total cost will your Building Operations department be held accountable for (charged with) for performance evaluation purposes?

Answers: 3


Another question on Business

Business, 21.06.2019 19:50
Suppose your rich uncle gave you $50,000, which you plan to use for graduate school. you will make the investment now, you expect to earn an annual return of 6%, and you will make 4 equal annual withdrawals, beginning 1 year from today. under these conditions, how large would each withdrawal be so there would be no funds remaining in the account after the 4th?
Answers: 1

Business, 21.06.2019 22:30
An annuity that goes on indefinitely is called a perpetuity. the payments of a perpetuity constitute a/an series. the equation is: a stock with no maturity is an example of a perpetuity. quantitative problem: you own a security that provides an annual dividend of $170 forever. the security’s annual return is 9%. what is the present value of this security? round your answer to the nearest cent. $
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 06:00
Select the correct answer a research organization conducts certain chemical tests on samples. they have data available on the standard results. some of the samples give results outside the boundary of the standard results. which data mining method follows a similar approach? o a. data cleansing ob. network intrusion o c. fraud detection od. customer classification o e. deviation detection
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 12:50
Required information problem 15-1a production costs computed and recorded; reports prepared lo c2, p1, p2, p3, p4 [the following information applies to the questions displayed below. marcelino co.'s march 31 inventory of raw materials is $84,000. raw materials purchases in april are $540,000, and factory payroll cost in april is $364,000. overhead costs incurred in april are: indirect materials, $59,000; indirect labor, $26,000; factory rent, $38,000; factory utilities, $19,000; and factory equipment depreciation, $58,000. the predetermined overhead rate is 50% of direct labor cost. job 306 is sold for $670,000 cash in april. costs of the three jobs worked on in april follow. job 306 job 307 job 308 balances on march 31 direct materials $30,000 $36,000 direct labor 25,000 14,000 applied overhead 12,500 7,000 costs during april direct materials 133,000 210,000 $100,000 direct labor 105,000 150,000 101,000 applied overhead ? ? ? status on april 30 finished (sold) finished in process (unsold) required: 1. determine the total of each production cost incurred for april (direct labor, direct materials, and applied overhead), and the total cost assigned to each job (including the balances from march 31). a-materials purchases (on credit). b-direct materials used in production. c-direct labor paid and assigned to work in process inventory. d-indirect labor paid and assigned to factory overhead. e-overhead costs applied to work in process inventory. f-actual overhead costs incurred, including indirect materials. (factory rent and utilities are paid in cash.) g-transfer of jobs 306 and 307 to finished goods inventory. h-cost of goods sold for job 306. i-revenue from the sale of job 306. j-assignment of any underapplied or overapplied overhead to the cost of goods sold account. (the amount is not material.) 2. prepare journal entries for the month of april to record the above transactions. 3. prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. 4.1 compute gross profit for april. 4.2 show how to present the inventories on the april 30 balance sheet.
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Fabricating and Finishing are two production departments of Michael Manufacturing. Building Operatio...
Questions












Mathematics, 29.06.2019 05:10








Physics, 29.06.2019 05:10



