Business, 06.05.2020 08:31 Kikilcaro9675
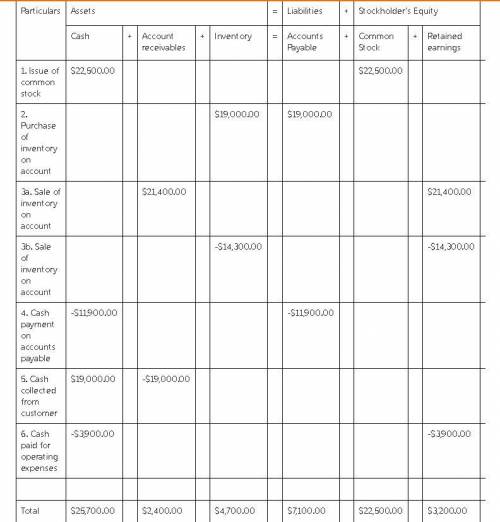
During 2018, Hardy Merchandising Company purchased $19,000 of inventory on account. Hardy sold inventory on account that cost $14,300 for $21,400. Cash payments on accounts payable were $11,900. There was $19,000 cash collected from accounts receivable. Hardy also paid $3,900 cash for operating expenses. Assume that Hardy started the accounting period with $22,500 in both cash and common stock.
Required:
a. Record the events in a horizontal statement model. In the Cash Flow column, use OA to designate operating activity, IA for investment activity, FA for financing activity, or NC for net change in cash. If the element is not affected by the event, leave the cell blank. What is the balance of accounts receivable at the end of 2018?
b. What is the balance of accounts payable at the end of 2016?
c. What are the amounts of gross margin and net income for 2016?
d. Determine the amount of net cash flow from operating activities. (Indicate cash outflows with minus sign.)

Answers: 2


Another question on Business

Business, 22.06.2019 17:00
You hold a diversified $100,000 portfolio consisting of 20 stocks with $5,000 invested in each. the portfolio's beta is 1.12. you plan to sell a stock with b = 0.90 and use the proceeds to buy a new stock with b = 1.50. what will the portfolio's new beta be? do not round your intermediate calculations.
Answers: 2

Business, 22.06.2019 20:40
Consider an economy where the government's budget is initially balanced. the production function, consumption function and investment function can be represented as follows y equals k to the power of alpha l to the power of 1 minus alpha end exponent c equals c subscript 0 plus b left parenthesis y minus t right parenthesis i equals i subscript 0 minus d r suppose that taxes increase. what happens to the equilibrium level of output?
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 21:10
Match the terms with their correct definition. terms: 1. accounts receivable 2. other receivables 3 debtor 4. notes receivable 5. maturity date 6. creditor definitions: a. the party to a credit transaction who takes on an obligation/payable. b. the party who receives a receivable and will collect cash in the future. c. a written promise to pay a specified amount of money at a particular future date. d. the date when the note receivable is due. e. a miscellaneous category that includes any other type of receivable where there is a right to receive cash in the future. f. the right to receive cash in the future from customers for goods sold or for services performed.
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 21:30
Russell's study compared gpa of those students who volunteered for academic study skills training and those who did not elect to take the training. he found that those who had the training also had higher gpa. with which validity threat should russell be most concerned?
Answers: 2
You know the right answer?
During 2018, Hardy Merchandising Company purchased $19,000 of inventory on account. Hardy sold inven...
Questions

History, 09.11.2020 06:10


Biology, 09.11.2020 06:10



Mathematics, 09.11.2020 06:10



Mathematics, 09.11.2020 06:10



Mathematics, 09.11.2020 06:10




Mathematics, 09.11.2020 06:10




Computers and Technology, 09.11.2020 06:10