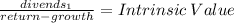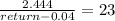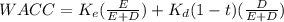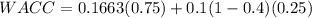Business, 17.08.2019 22:20 gerardogonzale362
Empire electric company (eec) uses only debt and common equity. it can borrow unlimited amounts at an interest rate of rd = 10% as long as it finances at its target capital structure, which calls for 25% debt and 75% common equity. its last dividend (d0) was $2.35, its expected constant growth rate is 4%, and its common stock sells for $23. eec's tax rate is 40%. two projects are available: project a has a rate of return of 13%, and project b's return is 9%. these two projects are equally risky and about as risky as the firm's existing assets. a. what is its cost of common equity? round your answer to two decimal places. do not round your intermediate calculations. b. what is the wacc? round your answer to two decimal places. do not round your intermediate calculations. c. which projects should empire accept?

Answers: 2


Another question on Business

Business, 21.06.2019 18:20
Amathematical approximation called the rule of 70 tells us that the number of years that it will take something that is growing to double in size is approximately equal to the number 70 divided by its percentage rate of growth. thus, if mexico's real gdp per person is growing at 7 percent per year, it will take about 10 years(=70/7) to double. apply the rule of 70 to solve the following problem. real gdp per person in mexico in 2005 was about $11,000 per person, while it was about $44,000 per person in the u.s. if real gdp per person in mexico grows at the rate of 5 percent per year: how long will it take mexico's real gdp per person to reach the level that the united states was at in 2005? (hint: how many times would mexico's 2005 real gdp per person have to double to reach the u.s.'s 2005 real gdp per person?
Answers: 3

Business, 22.06.2019 01:00
The law says your employer is responsible for providing you with a safe and healthy workplace. true or false?
Answers: 1

Business, 22.06.2019 20:50
The following accounts are from last year’s books at s manufacturing: raw materials bal 0 (b) 157,400 (a) 172,500 15,100 work in process bal 0 (f) 523,600 (b) 133,700 (c) 171,400 (e) 218,500 0 finished goods bal 0 (g) 477,000 (f) 523,600 46,600 manufacturing overhead (b) 23,700 (e) 218,500 (c) 27,700 (d) 159,400 7,700 cost of goods sold (g) 477,000 s manufacturing uses job-order costing and applies manufacturing overhead to jobs based on direct labor costs. what is the amount of cost of goods manufactured for the year
Answers: 3

Business, 23.06.2019 00:30
Activity-based costing (abc) is not truly a cost collection mechanism as much as it is an inventory valuation method. the main purpose for implementing an activity-based cost system is to try to overcome some of the cost distortions that occur in traditional costing from product differences when there are variations in size and complexity. however, one of the disadvantages of utilizing abc is that the additional information gathering necessary to implement costing with that level of detail might be beyond the reach of some companies with resource or financial constraints. with this in mind, what kinds of industries or companies do you think would benefit most from using activity-based costing and why? in designing or modifying an accounting system to capture appropriate costs for abc, what considerations do you think would need to be made?
Answers: 3
You know the right answer?
Empire electric company (eec) uses only debt and common equity. it can borrow unlimited amounts at a...
Questions





Physics, 20.10.2020 02:01


Health, 20.10.2020 02:01


History, 20.10.2020 02:01

Mathematics, 20.10.2020 02:01



Social Studies, 20.10.2020 02:01


Mathematics, 20.10.2020 02:01


German, 20.10.2020 02:01

Mathematics, 20.10.2020 02:01


English, 20.10.2020 02:01