Using the Scientific Method
This activity will help you meet this educational goal:
You will...

Biology, 30.10.2021 17:50 genyjoannerubiera
Using the Scientific Method
This activity will help you meet this educational goal:
You will plan an investigation using the scientific method and answer the proposed questions.
Directions
Read the instructions for this self-checked activity. Type in your response to each question, and check your answers. At the
end of the activity, write a brief evaluation of your work.
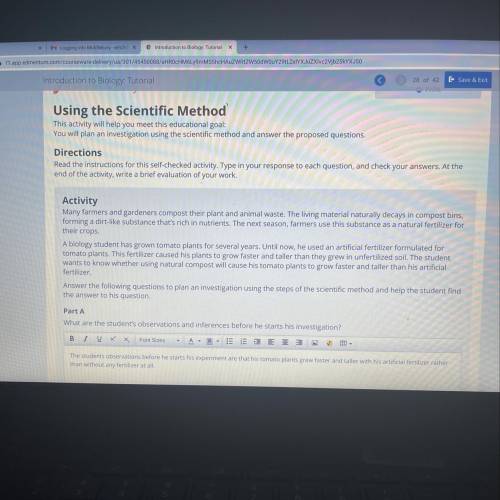
Activity
Many farmers and gardeners compost their plant and animal waste. The living material naturally decays in compost bins,
forming a dirt-like substance that's rich in nutrients. The next season, farmers use this substance as a natural fertilizer for
their crops.
A biology student has grown tomato plants for several years. Until now, he used an artificial fertilizer formulated for
tomato plants. This fertilizer caused his plants to grow faster and taller than they grew in unfertilized soil. The student
wants to know whether using natural compost will cause his tomato plants to grow faster and taller than his artificial
fertilizer
Answer the following questions to plan an investigation using the steps of the scientific method and help the student find
the answer to his question.
Part A
What are the student's observations and inferences before he starts his investigation?
B IV x x Font Sizes A- A - E 1 E 3
The students observations before he starts his experiment are that his tomato plants grew faster and taller with his artificial fertilizer rather
than without any fertilizer at all

Answers: 3


Another question on Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:30
Match the descriptions / definitions with the term they best describe 1. three dimensional relationship of the different polypeptide chains in a multisubunit protein or protein complex 2. common folding pattern in proteins in which a linear sequence of amino acids folds into a right-handed coil stabilized by internal hydrogen-bonding between polypeptide backbone atoms. 3. the amino acid sequence of a protein 4. a region on the surface of a protein that can interact with another molecule through noncovalent bonding. 5. three-dimensional arrangement of alpha-helices and beta-sheets within a single polypeptide, typically stabilized by a variety of noncovalent bonds, including ionic and hydrogen bonds, and nonpolar interactions / hydrophobic force. 6. the chain of repeating carbon and nitrogen atoms, linked by peptide bonds, in a protein. 7. common structural motif in proteins in which different sections of the polypeptide chain run alongside each other and are joined together by hydrogen bonding between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. 8. portion of a polypeptide chain that has a discrete tertiary structure of its own and can often fold independently of the rest of the chain 9. regular local folding patterns in a protein, including alpha-helix and beta-sheet a. primary structure b. beta-sheet c. protein d. coiled-coil e. polypeptide backbone f. secondary structure g. side chain h. tertiary structure i. binding site j. alpha-helix k. quaternary structure l. protein domain
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 03:00
Which of the following is the source of energy for photosynthesis? a.) glucose b.) chlorophyll c.) carbon dioxide d.) sunlight
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 05:10
Which of the following is not a potential result of deforestation?
Answers: 2

You know the right answer?
Questions


Mathematics, 15.01.2021 16:10




Chemistry, 15.01.2021 16:10

Chemistry, 15.01.2021 16:10

Computers and Technology, 15.01.2021 16:10

Arts, 15.01.2021 16:10

Mathematics, 15.01.2021 16:10

Chemistry, 15.01.2021 16:10



Mathematics, 15.01.2021 16:10

Physics, 15.01.2021 16:10


Physics, 15.01.2021 16:10