
Biology, 30.10.2019 22:31 lanipooh01
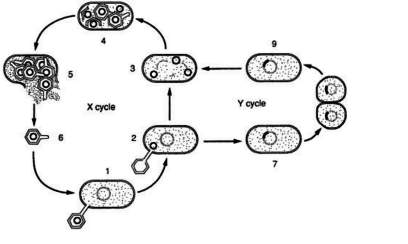
In the above diagram, which cycles represents lytic infection of a cell by a bacteriophage? (1 point)
x
y
both x and y
neither of the cycles
3. viruses containing rna as their genetic information are called (1 point)
retroviruses.
prophages.
bacteriophages.
capsids.
4. in the six-kingdom classification system, bacteria are divided into two kingdoms, eubacteria and archaebacteria. the main difference in the cell structures of the two groups of bacteria is that (1 point)
eubacteria do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, but archaebacteria do.
archaebacteria do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, but eubacteria do.
eubacteria have chlorophyll in their cells, but archaebacteria do not.
archaebacteria have chlorophyll in their cells, but eubacteria do not.
5. how do bacteria contribute to an ecosystem? (1 point)
some bacteria reduce the number of parasites infesting organisms in an ecosystem.
some bacteria provide nutrients and raw materials for organisms in an ecosystem.
some bacteria are a primary food source for most of the consumers in an ecosystem.
some bacteria provide protection from viral infections for the organisms in an ecosystem.
6. which of the following roles of bacteria is not a benefit to human bodies? (1 point)
digesting food
preventing diabetes
making vitamins
acting as a pathogen
7. two ways bacteria cause disease is by using the cells of the organism they infect as food and by (1 point)
making antibiotics.
releasing toxins.
releasing viruses.
releasing disinfectants.
8. antibiotics are often effective treatments for diseases caused by (1 point)
bacteria.
viruses.
some bacteria and some viruses.
all bacteria and all viruses.
9. what is one reason biologists have difficulty classifying protists? (1 point)
protists are eukaryotes just as plants, fungi, and animals are.
protists are incredibly diverse, and the different groups probably evolved independently of each other.
protists belong in the same classification group as bacteria.
protists were the first eukaryotes, and they appeared nearly 1.5 billion years ago.
10. ciliates can reproduce asexually using fission, but they can also exchange genetic material with one another. what is this process called? (1 point)
budding
colonisation
conjugation
parasitism
11. in protozoans, for what are the structures called cilia and pseudopods used? (1 point)
respiration and movement, respectively
movement and feeding, respectively
feeding and excretion, respectively
excretion and respiration, respectively
12. which member of the kingdom fungi is not multicellular? (1 point)
yeasts
algae
slime moulds
rusts
13. the tangled mass that makes up the body of a fungus is the (1 point)
hypha.
rhizoid.
mycelium.
stolon.
14. the cell walls of fungi differ from those of plants and protists because the cell walls of fungi (1 point)
are composed of cellulose.
are composed of peptidoglycan.
are composed of chitin.
contain chlorophyll.
15. how does symbiosis benefit the organisms that make up a lichen? (1 point)
each organism absorbs minerals produced by the other.
it reduces the effect of pollution and other toxic chemicals on both organisms.
it allows the organisms to live in environments where neither could live alone.
one organism eats the other to provide chemicals or nutrients missing from its environment.
16. plant roots can gain important materials through symbiotic relationships with fungi. what are these associations called? (1 point)
euglenoids
lichens
mycelia
mycorrhizae
17. with rare exceptions, which of the following characteristics do plants share? (1 point)
unicellular
flowering
prokaryotic
autotrophic
18. which statement describes the sizes of nonvascular and vascular plants? (1 point)
plants of both groups are about the same size.
nonvascular plants are typically smaller than vascular plants.
vascular plants are usually smaller than nonvascular plants.
there are no observable patterns in the sizes of the two groups.
19. what effect did the development of vascular tissue have on plant evolution? (1 point)
the development of vascular tissue allowed plants to grow taller.
the development of vascular tissue allowed plants to colonise wetter environments.
the development of vascular tissue reduced the reliance on water for reproduction.
the development of vascular tissue aided with the dispersal of offspring.
20. the chemical lignin hardens plants' cell walls. what does this allow plants to do? (1 point)
stand upright
exist without water
perform photosynthesis
obtain nitrogen from the soil
21. which group of plants evolved first? (1 point)
angiosperms
gymnosperms
ferns
mosses


Answers: 1


Another question on Biology


Biology, 22.06.2019 00:30
At which location in earth’s interior does the top density continue to increase as thickness decreases?
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 03:00
What best describes the structure of the declaration of independence?
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 04:00
Will mark brainliest i only need the ! 1.use ten beads and a centromere of one color to construct the long chromosome. use ten beads and a centromere of a second color to construct the second chromosome in the long pair. make a drawing of the chromosomes in the space below. 2. for the second pair of chromosomes, use only five beads. 3. now model the replication of the chromosomes. make a drawing of your model in the space below. part b: meiosis i during meiosis i, the cell divides into two diploid daughter cells. 4. pair up the chromosomes to form tetrads. use the longer tetrad to model crossing-over. make a drawing of the tetrads in the space below. 5. line up the tetrads across the center of your “cell.” then model what happens to the chromosomes during anaphase i. 6. divide the cell into two daughter cells. use the space below to make a drawing of the result. part c: meiosis ii during meiosis ii, the daughter cells divide again. 7. line up the chromosomes at the center of the first cell, one above the other. separate the chromatids in each chromosome and move them to opposite sides of the cell. 8. repeat step 7 for the second cell. 9. divide each cell into two daughter cells. use the space below to make a drawing of the four haploid cells
Answers: 1
You know the right answer?
In the above diagram, which cycles represents lytic infection of a cell by a bacteriophage? (1 poin...
Questions


Mathematics, 18.09.2021 14:40


Biology, 18.09.2021 14:40




Chemistry, 18.09.2021 14:50




Mathematics, 18.09.2021 14:50


Mathematics, 18.09.2021 14:50


Chemistry, 18.09.2021 14:50


Mathematics, 18.09.2021 14:50


Mathematics, 18.09.2021 14:50



